 Część dalsza czasów przeszłych. Panie i Panowie, przed nami czasy zaprzeszłe :)))
Część dalsza czasów przeszłych. Panie i Panowie, przed nami czasy zaprzeszłe :)))
‘I wonder if you’ve got such a thing as a balloon about you?’
‘A balloon?’
‘Yes, I just said to myself coming along: “I wonder if Christopher Robin has such a thing as a balloon about him?” I just said it to myself, thinking of balloons, and wondering.’
‘What do you want a balloon for?’ you said.
Winnie-the-Pooh looked round to see that nobody was listening, put his paw to his mouth, and said in a
deep whisper: ‘Honey!’
‘But you don’t get honey with balloons!’
‘I do,’ said Pooh.
Well, it just happened that you had been to a party the day before at the house of your friend Piglet, and you had balloons at the party. You had had a big green balloon; and one of Rabbit’s relations had had a big blue one, and had left it behind, being really too young to go to a party at all; and so you had brought the green one and the blue one home with you.
...
...
And all the time Winnie-the-Pooh had been trying to get the honey-jar off his head. Themore he shook it, the more tightly it stuck. "Bother!" he said, inside the jar, and "Oh, help!" and, mostly, "Ow!" And he tried bumping it against things, but as he couldn't see what he was bumping it against, it didn't help him; and he tried to climb out of the Trap, but as he could see nothing but jar, and not much of that, he couldn't find his way. So at last he lifted up his head, jar and all, and made a loud, roaring noise of Sadness and Despair . . . and it was at that momentthat Piglet looked down.
Winnie-the Pooh A.A. Milne
Past Perfect Simple | Past Perfect Continuous |
Budowa | |
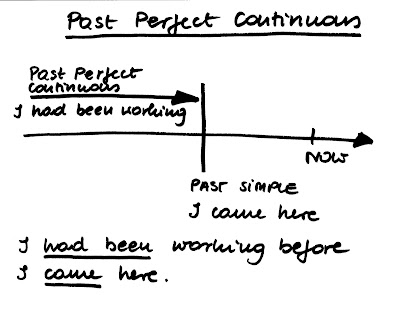
HAD(N’T) + 3rd Form I had been to the supermarket before I came here. Byłem w supermarkecie zanim tutaj przyszedłem. | HAD(N’T) + BEEN + VERB + ING I had been working before I came here. Pracowałem zanim tutaj przyszedłem. |
Kiedy używamy | |
Obu czasów zaprzeszłych używamy wtedy gdy musimy opisać coś, co wydarzyło się przed jakimś przeszłym wydarzeniem. | |
Czas Past Perfect Simple opisuje dokonane wydarzenia które miały miejsce przed jakimś punktem w przeszłości: Before I took part in the marathon I had competed in several minor running competitions. Zanim wziąłem udział w maratonie wystartowałem w kilku mniejszych biegach. | Czas Past Perfect Continuous opisuje niedokonane czynności które działy się do pewnego momentu w przeszłości: Before I took part in the marathon I had been running for 3 years. Zanim wziąłem udział w maratonie biegałem trzy lata. |
Czas Past Perfect Simple może opisywać wydarzenie któro miało jakiś określony rezultat lub skutek w przeszłości: Tom was late because his car had broken down. Tom się spóźnił ponieważ zepsuł mu się samochód. | Czas Past Perfect Continuous może opisywać czynność której efekty uboczne były widoczne w przeszłości: Bob was exhausted because he had been running. Bob był wyczerpany ponieważ biegał. |
Czas Past Perfect Simple może zwracać uwagę na to ile czegoś zostało zrobione, czyli będzie podkreślał LICZBĘ: I had run 5 km before I broke my leg. Przebiegłem 5 km zanim złamałem nogę. | Czas Past Perfect Continuous może zwracać uwagę na to jak długo trwało wykonywanie danej czynności, czyli będzie podkreślał TRWANIE lub CZAS: I had been running for a few months before I broke my leg. Biegałem kilka miesięcy zanim złamałem nogę. |
O czym warto pamiętać | |
Czasy Past Perfect są używane wtedy gdy mamy jakiś punkt odniesienia w przeszłości (przed którym coś się wydarzyło lub działo) wyrażony za pomocą czasu Past Simple: I had met Sue before I went to work. (Past Perfect + before + Past Simple) Zatem zdanie typu: Nie ma racji bytu! Powinno być zbudowane za pomocą Past Simple: I met Sue yesterday. | |
Kiedy opisujemy przeszłe dokonane wydarzenia zachowując chronologię wydarzeń, to nie potrzebujemy Past Perfect, wystarczy sam Past Simple: I finished work, called Sue and went home. | |
Kiedy mamy w zdaniu ALREADY używamy bezwzględnie Past Perfect Simple: When I arrived at the party, Lucy had already gone home. | |
Są przypadki kiedy użycie czasu Past Perfect nie jest obowiązkowe ale zazwyczaj się go używa ;) After he (had) finished his exams he went to Paris. She didn’t feel the same after her husband (had) died. | |
Czasów Past Perfect używamy w przeróżnych konstrukcjach gramatycznych tj. zdania warunkowe (trzecie i mieszane), konstrucje z WISH czy też mowa zależna. | |











0 komentarze:
Prześlij komentarz